Payroll management is an intricate and integral aspect of any organization’s financial management. It involves the calculation, disbursement, and recording of employee compensation, including wages, salaries, bonuses, and deductions. The process is pivotal, as it ensures that employees are paid accurately, consistently, and on time, while adhering to various tax regulations and labor laws. This guide provides an in-depth exploration of payroll, spanning its definition, the stages of processing, key challenges, various methods for execution, the significance of payroll software, and the choice between cloud-based solutions and on-premise alternatives.
What is Payroll?
Payroll, in its essence, is the financial process within an organization that manages the distribution of employee compensation. This compensation encompasses various elements, such as basic salaries, hourly wages, overtime pay, bonuses, commissions, and deductions for taxes and benefits. It is one of the most fundamental functions for any organization, regardless of size or industry.
The Importance of Payroll Management
The significance of payroll is paramount. It directly impacts the livelihood of employees, their job satisfaction, and the overall financial health of the organization. Accuracy and timeliness are imperative, as errors can lead to legal consequences, employee dissatisfaction, and financial complications.
Stages of Processing Payroll
Processing payroll is a multi-step procedure that includes pre-payroll activities, the actual payroll process, and post-payroll activities. These stages work together to ensure that payroll is managed efficiently and accurately.
- Pre-Payroll Activities
The initial stage, pre-payroll activities, involves gathering, verifying, and organizing employee data. This data encompasses details on working hours, attendance records, changes in personal or financial information, and other factors that impact compensation. Additionally, pre-payroll activities include calculations for various deductions, such as taxes and benefits. Ensuring compliance with tax laws, labor regulations, and internal policies is a primary concern during this stage.
- The Actual Payroll Process
The core of payroll management, the actual payroll process, executes the calculations and data processing necessary to generate precise paychecks or direct deposits. Key components include the precise computation of gross pay, which factors in the base salary or hourly wage, as well as any additional compensation like overtime pay or bonuses. Deductions, including taxes, retirement contributions, and benefits, are meticulously calculated, culminating in the net pay received by employees. This process is comprehensive and considers various employee-specific factors, such as leaves of absence and other variable components that may affect compensation. Furthermore, it includes the creation of paychecks or electronic fund transfers, ensuring the accurate and timely payment of employees.
- Post-Payroll Process
The final stage, post-payroll activities, serves to tie up loose ends and ensure all transactions are accurately recorded. This stage includes the generation of payslips for employees, which provide a breakdown of their compensation, deductions, and any additional information related to their pay. In addition, post-payroll activities encompass the preparation of financial reports that are vital for the organization’s record-keeping and auditing processes. It is essential to record all payroll transactions accurately and in a way that aligns with the organization’s financial system and accounting standards. This is crucial for maintaining an accurate and transparent record of financial operations.
Challenges in Handling Payroll Management
While payroll is essential, it is not without its challenges. Organizations often encounter various obstacles when managing payroll. These challenges can include:
Errors:- Manual payroll processing is susceptible to errors, which can have significant consequences, including underpayment or overpayment of employees. Such errors can lead to dissatisfaction among employees and harm an organization’s reputation.
Compliance:- Staying up to date with evolving tax laws and labor regulations is a continuous challenge. Non-compliance can result in financial penalties and legal issues for organizations. Adhering to these regulations requires continuous monitoring and adaptation.
Data Security:- Handling sensitive employee information, such as Social Security numbers and bank details, can pose data security risks if not managed properly. Data breaches can have severe consequences, including financial loss and damage to an organization’s reputation.
Time-Consuming:- Manual payroll processing is time-consuming, especially for organizations with a large workforce. This can divert resources and attention from other critical HR and business functions.
Inconsistency:- Manual methods may result in inconsistent payroll records, making it difficult for employees to understand their compensation. Consistency and transparency are essential for employee satisfaction and trust.
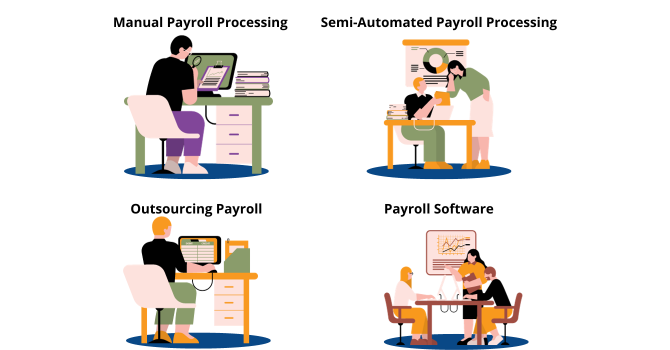
Various Methods Available to Do Payroll Management
There are several methods available for conducting payroll, ranging from manual and semi-automated approaches to fully automated payroll systems:
- Manual Payroll Processing
Manual payroll processing involves using spreadsheets, physical timecards, or paper records to manage employee compensation. While it may be cost-effective for very small businesses, it is prone to errors, time-consuming, and challenging to scale.
- Semi-Automated Payroll Processing
Semi-automated methods involve the use of software for certain aspects of payroll processing while retaining some manual tasks. This approach can help reduce errors and save time, but it may still lack the efficiency of fully automated systems.
- Outsourcing Payroll
Outsourcing payroll to a third-party provider is a popular option for many organizations. These providers handle the entire payroll process, including calculations, tax compliance, and record-keeping. While this can alleviate some payroll-related responsibilities, it may come with additional costs and reduced control over the process.
4. Payroll Software
Payroll software is a comprehensive solution that automates the entire payroll process. It includes features for calculating gross and net pay, handling deductions and benefits, generating payslips, and ensuring compliance with tax laws and labor regulations. Payroll software can be tailored to an organization’s specific needs and is an efficient and accurate way to manage payroll.
Best Payroll Software for Your Organization
Selecting the best payroll software for your organization requires careful consideration. The ideal software should possess the following characteristics:
Customization: The software should be customizable to align with your organization’s specific payroll structure, tax policies, and benefit plans.
Compliance Features: It should be up-to-date with the latest tax regulations and labor laws, ensuring seamless compliance with legal requirements.
User-Friendly Interface: An intuitive and user-friendly interface enhances user adoption and ease of use, reducing the learning curve for your HR and finance teams.
Support and Training: Choose a software provider that offers comprehensive support and training, helping you implement and use the software effectively.
Scalability: Evaluate whether the software can grow with your organization and accommodate future needs, particularly as your workforce expands.
Cloud-Based Software over On-Premise Solutions
The choice between cloud-based software and on-premise solutions is a pivotal consideration when implementing payroll software. Cloud-based payroll software offers several advantages over on-premise alternatives:
Accessibility: Cloud-based software is accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, allowing users to access payroll data and processes remotely.
Automatic Updates: Cloud-based solutions are automatically updated by the provider, ensuring that the software remains current and compliant with changing tax laws and labor regulations.
Reduced IT Infrastructure Costs: Cloud-based software eliminates the need for extensive on-site hardware and IT infrastructure, reducing costs and maintenance requirements.
Enhanced Security: Cloud-based payroll software providers invest in robust security measures, including data encryption and regular backups, to protect sensitive employee information.
Scalability: Cloud-based solutions are often more scalable, making them suitable for organizations with changing workforce sizes and needs.
In summary, payroll is a multifaceted and critical function for organizations. It involves various stages of processing, each of which contributes to ensuring accurate and timely employee compensation. Challenges, including errors, compliance, data security, and time constraints, underscore the importance of adopting efficient payroll methods and software solutions. The choice of the best payroll software for your organization should align with your specific needs, emphasizing customization, compliance, user-friendliness, support, and scalability. Cloud-based payroll software is increasingly favored for its accessibility, automatic updates, cost-effectiveness, security, and scalability, making it a contemporary choice for modern organizations.