Defining Performance Management System
Performance management system is also known as performance improvement system and refers to a system put in place to evaluate, monitor and enhance the performance of the people working in organizations. It entails defining expectations, feedback and appraisal, assessment of results and goal congruence of workers. It is meant to increase production, facilitate growth of personnel, as well as to catalyze organizational achievement.
A typical PMS (Performance Management System) includes features such as performance review tools, goal-setting tools, feedback mechanisms, and training/development modules. These tools help assess the organization’s current standing, drive performance improvement, promote accountability, and recognize achievements. An effective PMS enables HR professionals to track employee growth and adjust strategies to achieve the desired organizational outcomes.
Measurable parameters of performance management system:
- Goals: A performance management system has a goal at its base that is measurable and a definite target that particular individuals or teams attempt to attain. In doing so, an organization’s goals must be aligned with the overall organizational objectives which provide employees with clarity and direction.
- Reviews: Performance management system reviews are performance evaluations that are structured in purpose and usually conducted repeatedly (e.g. annually, twice yearly). They stem from giving evaluation, attending to phases where progress is being made, and doing so with due regard to your potential and weaknesses.
- Feedback: Feedback can be described as a two-way communication process that involves managers discussing the evaluation of their workers. It should be on time, concrete, and helpful, mostly focusing on the accomplished tasks but not excluding not or deadlocks. Feedback enables continuous and betterment.
- Development Plans: A development strategy lays down the deliberate steps that will be taken to sharpen an individual’s techniques, information, and skills. These plans could cover extensive training, practical classes, mentoring programs, or extended assignments targeting unique strengths and discoveries of the employee on the quest towards a career shift. Instructional designs focus on professional development directions and personal ambitions. These aspects are linked to organizational goals.
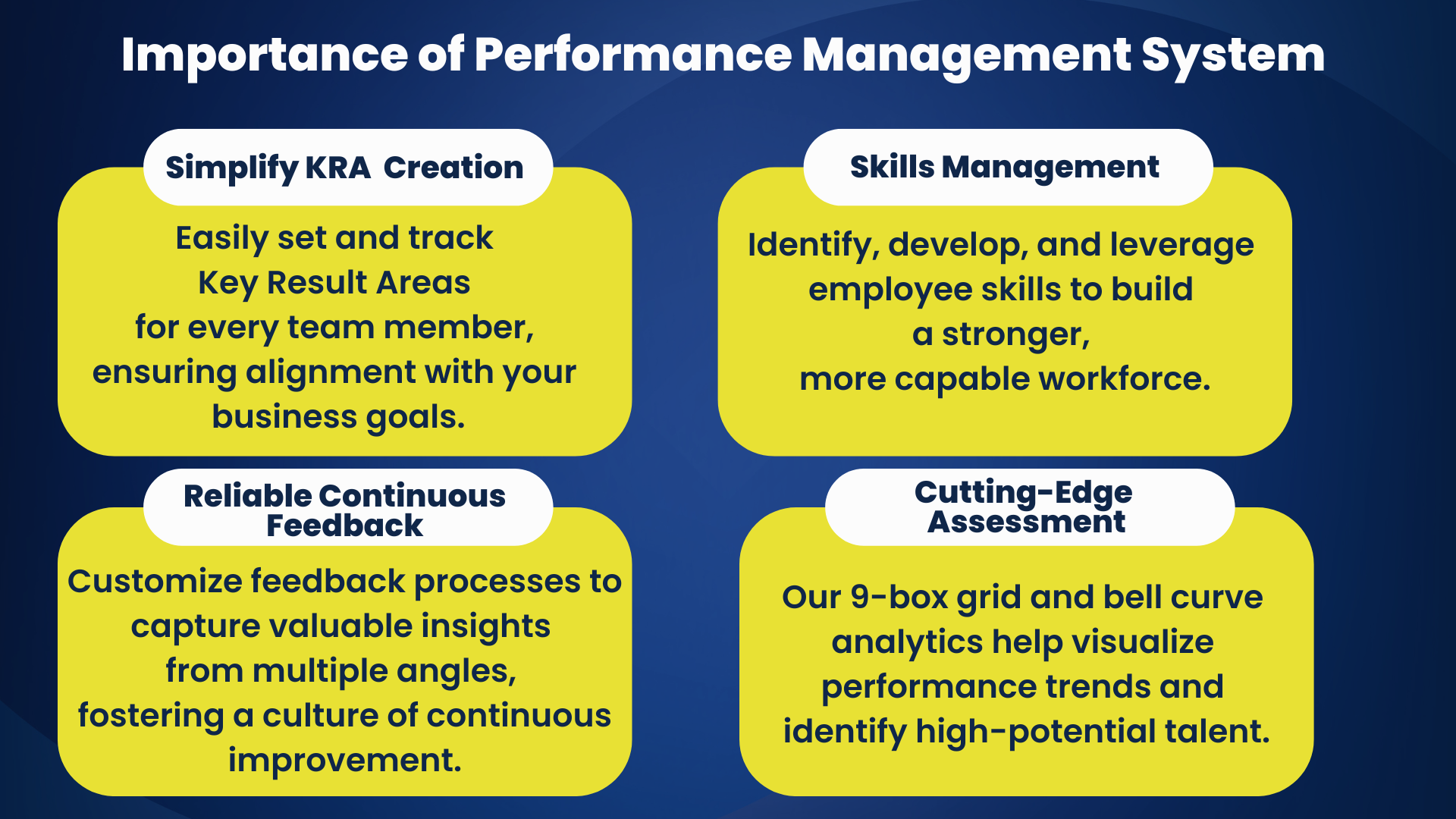
Importance of Performance Management System
The institution of an elaborate performance management system is one of the keys to organizational success since such a framework offers an organized approach to the handling of performance appraisal and employee development.
It facilitates the harmony of objectives between the teams at the workplace and the overall organization, thus letting employees know their purpose and direction in the organization.
Collaborative systems set up in which regular discussions and output are left form part of the comprehensive system, they contribute to the creation of transparency, clear evidence of a performance management system, and trust within the organization.
Employee engagement and motivation are enhanced through identification and acknowledgement of performance. Career development is also made possible through skill enhancement, and there are growth opportunities in the organization.
Also, the first aspect for the organization is the existence of a high level of performance management systems that allows to spot and resolve all performance inconsistencies beforehand which leads to greater productivity.
Key Components of Performance Management System:-
- Clear Objectives and Expectations: Of course, the common objective and performance expectations put this in place so that the employees can understand what is expected of them and how that aligns with organizational goals.
- Regular Feedback Mechanisms: Establishing feedback mechanisms makes ongoing communication possible, formal (eg. job reviews) and informal (eg. regular quick check-ins and exchanges) which helps team members to develop consistently.
- Structured Performance Reviews: Systematic performance management system reviews serve the purpose of assessing how far one has come so far, planning the next steps, and setting goals for the future.
- Individual Development Planning: Person development policies help employees become aware of the opportunities they can grab, and their ambitions and interests with organizational needs match.
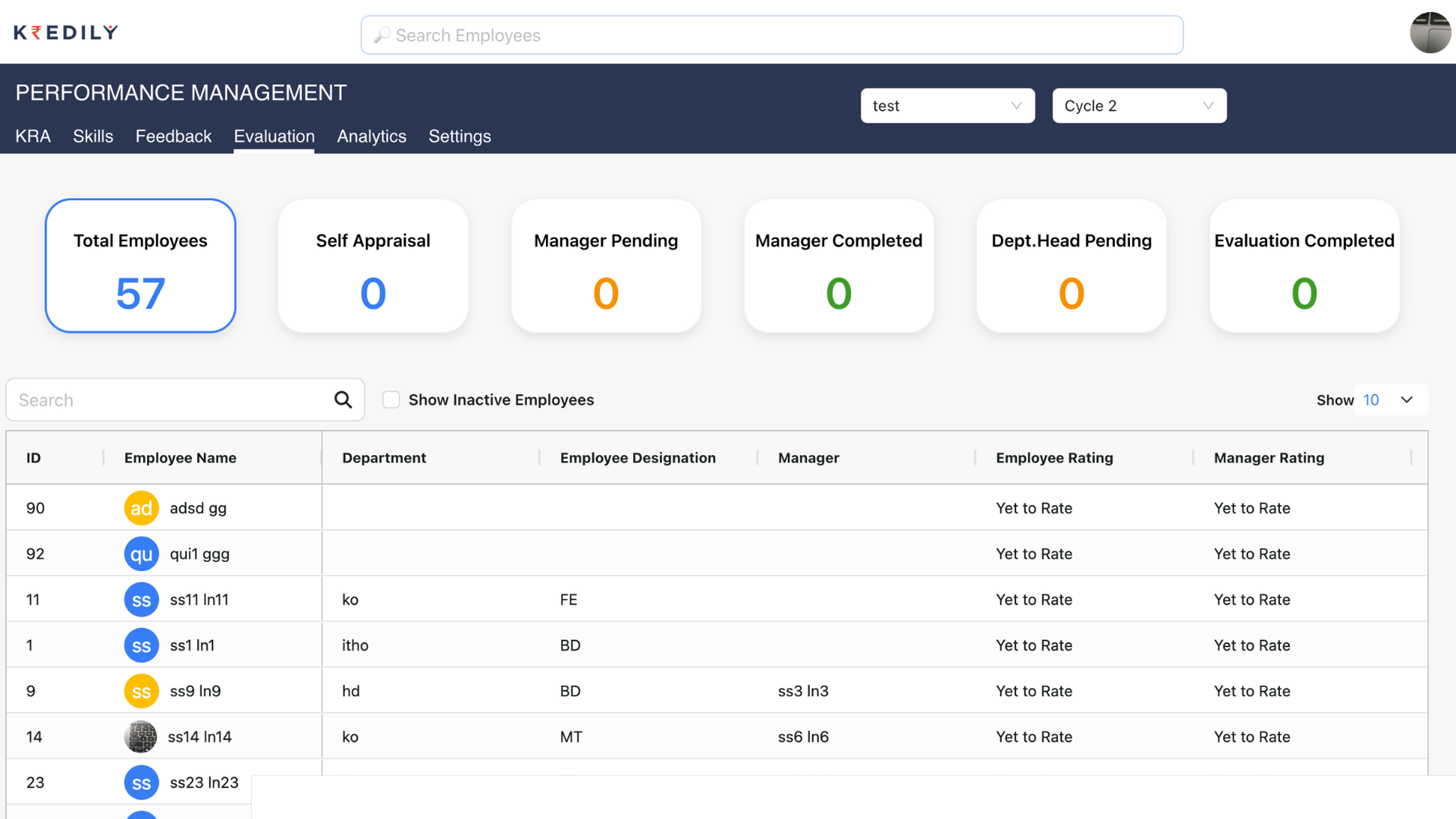
- Performance Management System Tools: Using technology and tools that can help the system automate the processes, track its performance metrics, and facilitate feedback and personal development activities raises the effectiveness and efficiency of the performance management system. A business process mining tool can also be used to analyze the underlying processes, offering insights into how these systems operate and where improvements may be needed.
- Training and Support: Managers and employees should go to training for better deliveries on performance management system processes and instruments to keep the consistency and gain the effectiveness of all organizations.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: Periodic reviewing and revamping the performance management system to make it responsive to suggestions and changes made from the feedback and reviews ensure the relevance and alignment of the framework to the organization’s goals.
How to Measure Performance Management System
Here’s a breakdown of the critical components that should be measured within a robust PMS:
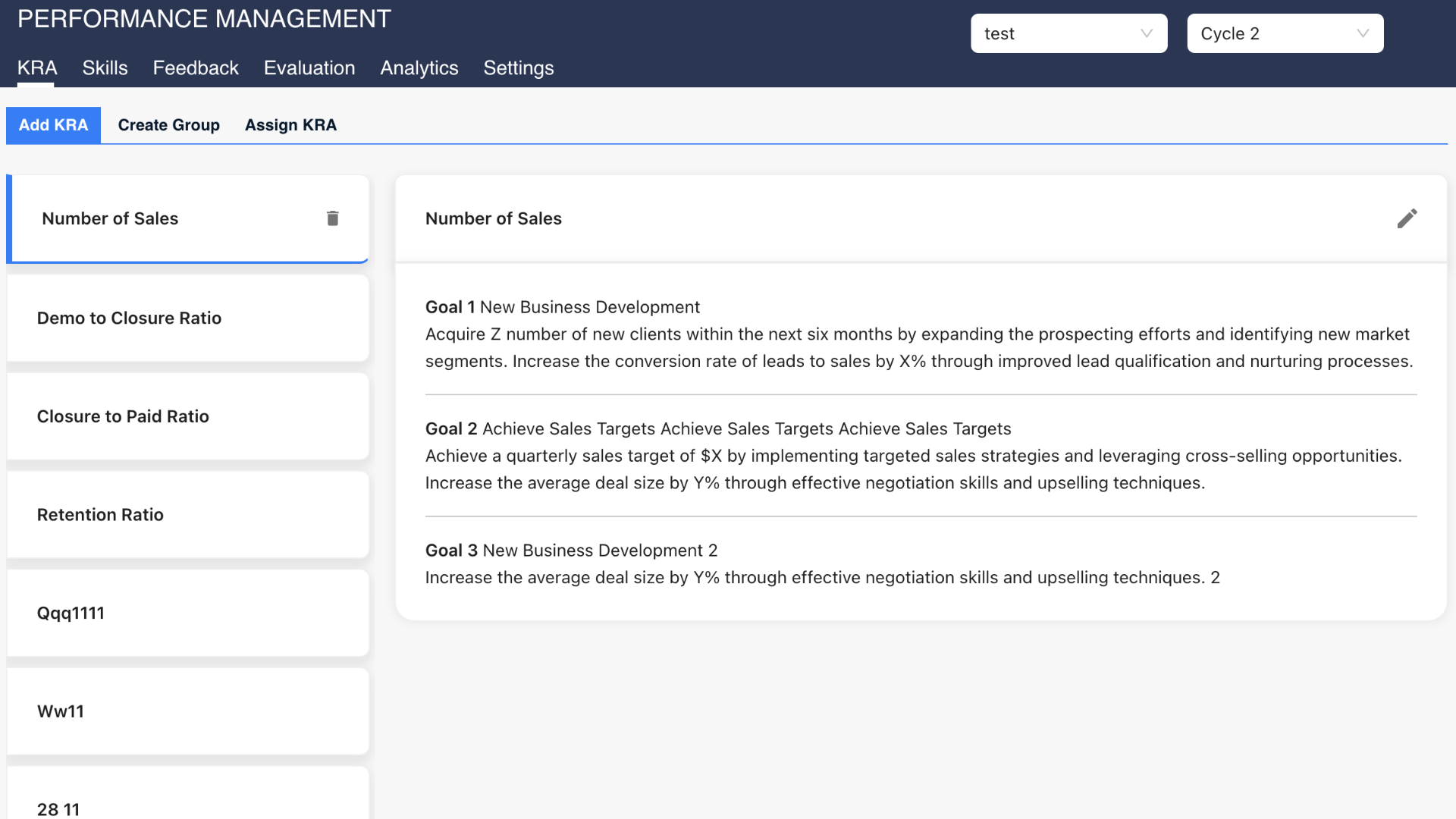
1. Key Result Areas (KRA)
Key Result Areas (KRAs) therefore define the precise, tangible results that an employee is to deliver within a given period of time. KRAs refer to an organisation and focus on outputs that support the same. The evaluation of KRAs facilitative the determination of whether employees are responding to their specific target and contributing to organizational objectives.
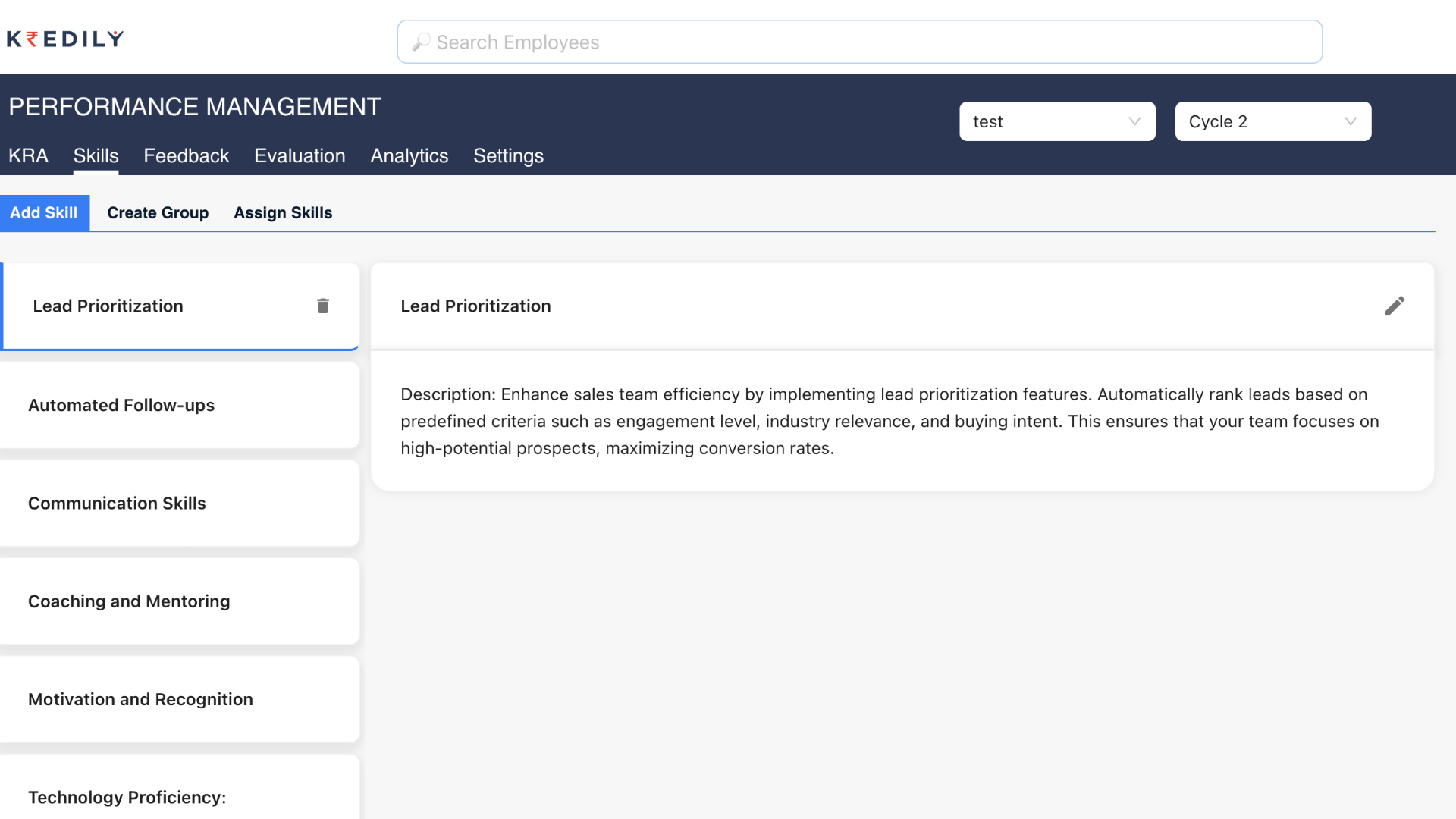
2. Skills and Competency Assessment
Checking employee skills and competencies is crucial in order to make certain that employees possess suitable skills to do their tasks adequately. This embraces expert knowledge specific to the job and other skills which are social in nature such as interpersonal, decisiveness, and negotiation skills. In the event, daily assessment of skills can help identify areas that require more practice or one on one training.
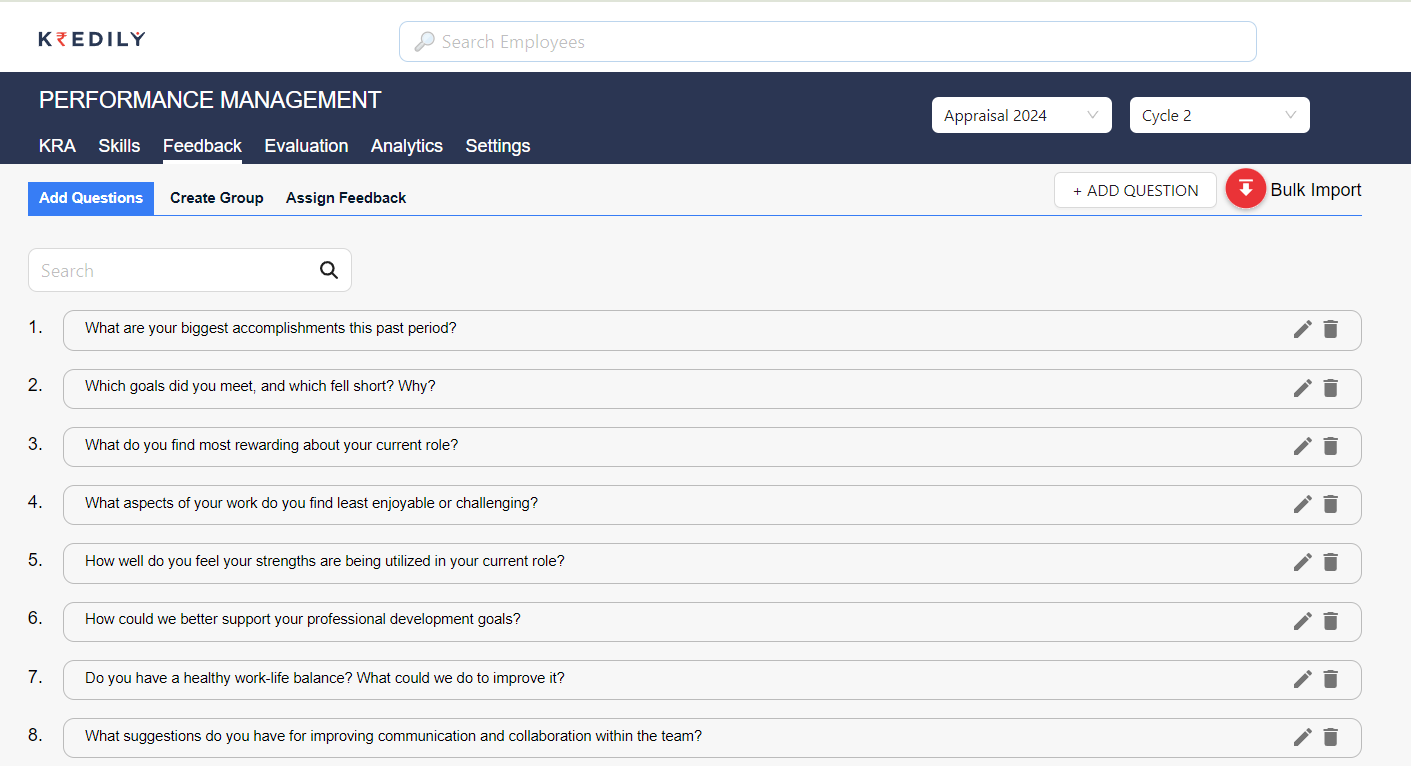
3. Performance Feedback Mechanisms
Constant feedback is one of the key attributes of performance management. Both giving and receiving feedback is a feature of the appraisal in the course of the cycle. Feedback makes it possible for employees to correct their performance in time and one is also able to know their mastery level.
4. Employee Evaluation
Performance appraisal is defined as the systematic assessment of one or more aspects of an employee’s performance at work. Ideally, the process occurs during performance evaluations, although it must be a constant cycle throughout an organization’s year.
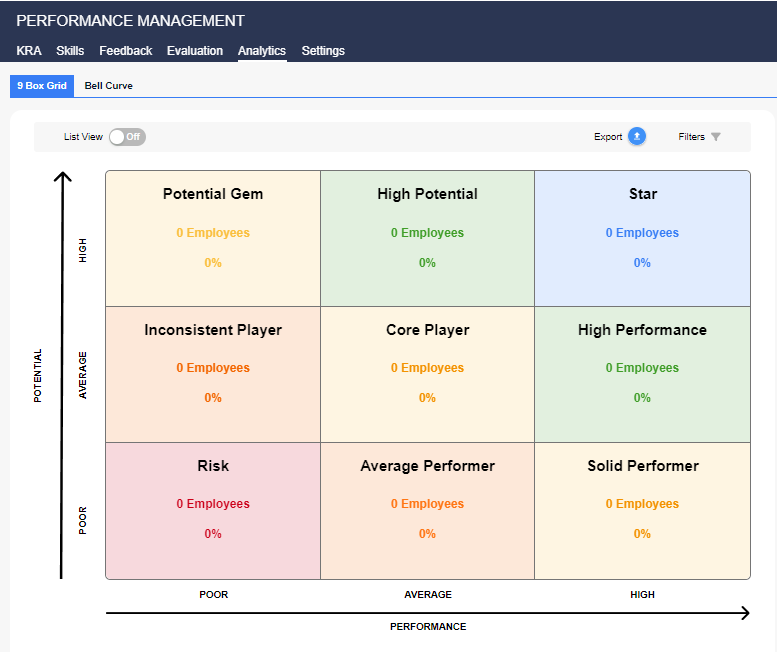
5. Analytics and Reporting
About performance management: analytics and data experience are crucial for today’s world. To be sure, HR analytics is a numerical tool to measure and discuss employee performance patterns and make appropriate conclusions. Potential, reassessment of performance, and overall evaluations of employee performance becomes much easier with performance data.
Assessing Your Current Performance Management System Process
It is all about taking an in-depth analysis of the performance evaluation process of the organization currently being followed. It involves checking how goals are made, how performance is reviewed, how feedback is given, and how advancement reads are written. Considering this review, an initial application can be evaluated and a starting point for performance management system evaluation for the organization can be identified
1. Reviewing Existing Performance Management System Tools:
Organizations frequently rely on the help of software and tools that provide easy ways of PA operations. Such analysis consists of the assessment of the appropriateness of these instruments to the improvement of the effectiveness of this management function. Factors, including simplicity of use, functionality, integration with existing systems, and the capacity to obtain the goal of the organization, are taken into consideration to check if the present tools are sufficient for the needs of the organization.
2. Evaluating the Efficiency of Current Performance Reviews:
The instrument of performance reviews is one of the most important tools, which calculates the efficiency of an employee and gives feedback. The evaluation is primarily concerned with the question of whether the performance review process is aligning the performance objectives with the corporate goals. Through evaluations of features like the frequency or structure of employee reviews, the quality of the feedback given & the consequent effectiveness of performance rating in employee development & institutional organization, it achieves this objective.
3. Identifying Gaps in Feedback Mechanisms:
In any employee excellence program, good feedback systems are what build the platform that employees can use for guidance and progress. Part of the game plan is to assess the organization’s gaps if there are any in their feedback processes. It involves measuring the achievability, the clarity, and the time requirement of feedback, which implies studying the channels of feedback. The process of recognition should involve uncovering the fundamental issues and providing subsequent measures to address them, thereby increasing employee productivity.
4. Assessing the Alignment of Development Plans with Organizational Goals:
Development plans not only reveal what steps the employees will pursue but also allow them to improve their skills and competencies. I.e., it needs to be ensured that these strategies are in line with the organization’s broader aims and objectives. This evaluation work requires going through individual development plan documents and determining whether they match the organization-wide purposes. It assures that every management maneuver becomes a productive extension helping the organization to achieve its set goals.
Setting Clear and Measurable Goals
Importance of Goal Setting in Performance Management:-
- Goal setting is not regarded lightly when it comes to performance management, as this leads to knowledge and understanding of what exactly is to be achieved by every employee.
- Manifesting precise goals empowers workers to distinguish their main tasks, concentrate their actions on them, and revitalize their efforts to achieve desired results.
- By establishing the goal of confidentiality leads to and adopts a culture of success through the members of the company, ultimately both the individuals and teams achieve the set goals.
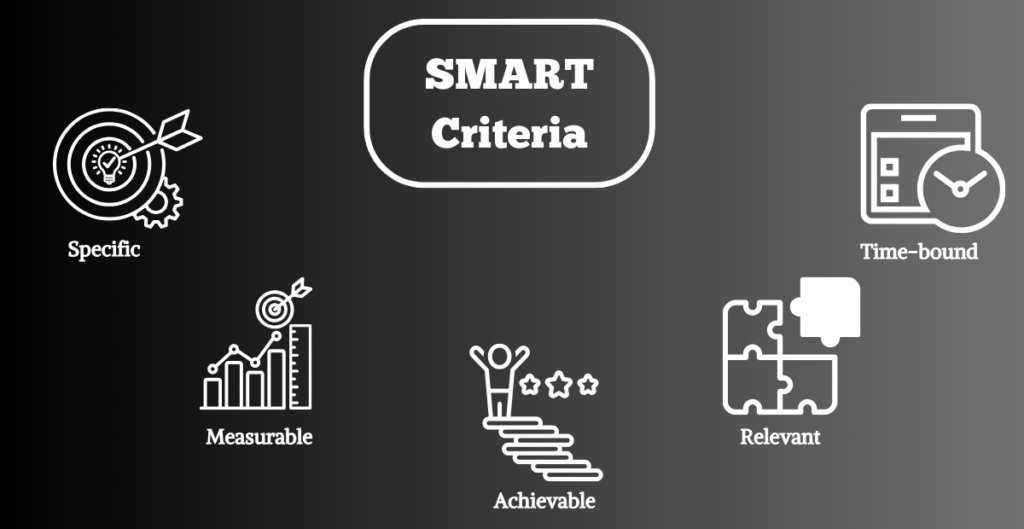
SMART Criteria for Setting Goals:
SMART is an acronym that consists of five letters, which are the initials of Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Aiming at It, and Time-bound.
- Specific: It’s A must that goals should be focused and clear, without any chance for vagueness.
- Measurable: The aim should be measurable so that it is possible to assess how close or far one can get and it can be accurately measured.
- Achievable: Goals should be thus realistic and attainable that they are concerned by the resources at hand and within the limitations imposed.
- Relevant: Objectives must mesh with overall organizational purposes, while also optimizing chances of business success.
- Time-bound: All the goals should be marked by a deadline or a discrete time frame, so they will force action without delay.
Utilizing Performance Management Tools for Goal Tracking:
- Performance management instruments are a key factor in creating goals, building up energy, and monitoring progress
- These tools allow the company’s staff and their managers to keep track of just what those are when they’re to be accomplished, and how that’s going along in real-time.
- Performance management program usually consists of such components as online goals dashboards, progress tracking tools, notifications, and reminders that feed performance, streamline goal-setting processes, and improve accountability.
Ensuring Alignment of Individual Goals with Organizational Objectives:
- All personal objectives must be in harmony and agreement with the overall, strategic, and fundamental goals of the organization so that there can be synergism and cohesion.
- When goal setting, individual employees and managers need to look into how they are helping in accomplishing management plans.
- The function of regular communication and feedback between employees and managers is vital and it guarantees that all priorities and goals at the individual level and the organizational level run parallel.
Conducting Effective Performance Reviews
Preparing for Performance Review Meetings:
All personal objectives must be in harmony and agreement with the overall, strategic, and fundamental goals of the organization so that there can be synergism and cohesion.
When goal setting, individual employees and managers need to look into how they are helping in accomplishing management plans.
The function of regular communication and feedback between employees and managers is vital and it guarantees that all priorities and goals at the individual level and the organizational level run parallel.
Providing Constructive Feedback Using Performance Management System Tools:
In the process of conducting a performance review, the manager has to use performance management system tools that are supposed to prevent getting mixed up with activities that do not contribute to the progress and lend a hand to provide structured and constructive feedback.
These instruments may take the following form: performance management system evaluation scoring table, digital platforms of informal feedback submission, or software that automates goal tracking.
Managers must zero in on case-specific cases, make their statement objective, and provide practical suggestions for the problems facing the employees in particular.
Addressing Strengths and Areas for Improvement:
Employee reviews should be noted all the time from their strengths to those that need to be improved.
The example for the staff should be set by managers. They should emphasize progress and success to enhance positive behaviour.
As managers, they should also make sure to discuss the part where the employee is short of performing their duties and they need to direct them on a process of improving.
Setting Actionable Plans Based on Review Outcomes:
After departmental evaluations, the managers and employees should set smart objectives that will be achieved in the next review session.
The plans must be created by keeping in mind the things that came out from the evaluation. We pay close attention to the strengths, spots of development, and career goals.
Objectives should define where, what, and when we need to do or add focus to particular things. They should be SMART and tandem with both personal and organizational goals as well.
The role of the manager includes the provision of resources, support, and feedback at the time of goal achievement for their development.
Leveraging Feedback Tools for Continuous Improvement
Understanding Different Feedback Mechanisms:
Spans provide feedback with a certain amount of formality as well as they come once a while, occasionally, and may be sourced from formal or informal routes. These may include such as formal performance reviews, through informal face-to-face meetings with a manager, 360-degree consensus from stakeholders and subordinates, surveys, and digital feedback systems.
Every device is unique in its approach having some specific utility and thus suitable for certain situations. The recognition of these inconsistencies is of great benefit to organizations as it enables them to select a particular feedback strategy for a specific purpose.
Integrating Real-time Feedback Tools into the Performance Management System Process:
Real-time evaluation systems currently provide employees with the possibility to receive extensive procurement on the spot, consequently allowing them the opportunity to make necessary changes and improvements in due time.
Through this medium, it is possible to loop them into performance management systems so that the manager and colleagues might give feedback on specific tasks, projects, or ethics as the event evolves.
Through the use of interactive feedback devices, organizations create avenues for moving forward, constant development, and agility.
Encouraging Peer-to-Peer Feedback:
Feedback in the peers’ environment comes when employees give feedback to colleagues. Moreover, audio feedback can be a great deal of help because it helps have different points of view and opinions.
Peer-to-peer feedback engages participation, incrementally reinforces the teamwork process, and instils the team loyalty culture.
Businesses are allowed to organize the feedback process among peers through structured feedback models, peer recognition programs, and team-based feedback sessions.
Incorporating Feedback into Ongoing Development Plans:
The proper controversy would be not to view it in isolation but in addition to the rest of the development process.
Employees and their immediate managers should hold a meeting after feedback sessions to develop and agree to implementation in the ongoing development together.
Developed plans will point to concrete actions and aim at providing ease of performance as well as additional feedback to improve it.
Through the incorporation of feedback into development plans organizations foster that the worth of the feedback is not just hypothetical but it is concrete and the performance and growth of the employee are enhanced.
Developing Customized Development Plans
Tailoring Development Plans to Individual Needs and Aspirations:
- Personalized job training programs emphasize that every employee possesses a particular array of skills and is not the same as one another in terms of their interests and professional goals.
- The plans will be formed as a result of a collaborative effort that will bring together employees and their managers to identify amongst others the areas that need improvement and development. These should be planned with due consideration taken to the individual’s aspirations and goals.
- Taking into consideration an employee’s personal development aims, making an address, in the same way, shows the right way to possibilities employees see.
Identifying Skill Gaps and Growth Opportunities:
- First of all, good developmental strategies ought to begin with the process of a detailed evaluation of an employee’s present abilities and competencies.
- On the one hand, managers and workers jointly pinpoint areas of skills gaps that call for more training, education, or even experience. On the other hand, a better position for employees could have been brought about by the capitalizing of growth opportunities.
- The shortfall of the skills and opportunities for growth can be identified which are of interest to both the individuals and the organization and therefore can be tailored.
Utilizing Performance Management Tools for Personalized Development Tracking:
- Performance management tools are vital in tracking and monitoring the progress made toward implementing development objectives.
- These tools equip the employees and managers by way of capturing development targets, tracking progress, and recording accomplishments over time.
- Through performance management tools, organizations will be able to make sure that development plans are evaluated adequately and tweaked if needed to support employee growth.
Establishing Milestones and Timelines for Skill Enhancement:
- The development plans must be specified in a way that goals and deadlines would be achieved, the monitoring of progress would be possible and the performance would anchor the participants of the process on that outcome.
- Milestones have concrete achievements or checkpoints at each learning stage, and on the other side, timelines are expected to complete each milestone at specific dates.
- Milestones and timelines help employees find the path for their development as well as allow managers to provide the support they need as they go about their learning journey.
Selecting and Implementing Performance Management System Tools
Researching and Evaluating Performance Management Software Options:
- Such work will be done by carrying out extensive surveys of current performance management system software packages to assess what is available.
- Organizations should do a review of solution features, functionalities, user reviews, and costs before choosing any particular software.
- Considering issues like feasibility, flexibility, and business capability can lead business to an enlightened decision.
Assessing Compatibility with Existing Systems and Processes:
- Firstly, before the deployment of performance management system software, it is important to assess its suitability in terms of the system and process environment of the organization.
- The evaluation will centre mainly on integrating this with other human resources systems like the payment system and employee registry.
- Compatibility is essential in all data transfer activities and implementation of equipment, as it allows for smooth data flow and minimizes disruptions.
Training Employees on Tool Utilization:
- Training can help to bring about a situation where employees can truly engage in the chosen performance management system tool.
- Organizations need to conduct complete training for the tools similar to working in a real environment and should teach employees the tool functionality, methods to navigate, and best practices.
- Training may come in various forms such as workshops, online tutorials, or individual sessions, and this can be determined based on the ease of use of the tool and the requirements of individuals.
Monitoring and Adjusting the Implementation Process for Optimal Results:
- The new tool for performance management system implementation will also need to perform continuous monitoring and changes for the best outcomes.
- Companies should devise KPIs( Key performance indicators) that will monitor how well the implementation plan is executed.
- Continuous evaluation enables institutions to identify any problematic issues and troubleshoot any bottleneck which would put a halt on any progress, therefore, improvement can be made to achieve outcomes.
- To make sure that the tool is meeting its purpose of empowering employees, you must gain feedback from the employees about the usability and effectiveness of this tool and use it to inform adjustments to the tool.